Wet Film Thickness (WFT) to Dry Film Thickness (DFT) Calculator
In the painting and coatings industry, achieving the right thickness is crucial for ensuring durability and aesthetic appeal. Understanding the relationship between Wet Film Thickness (WFT) and Dry Film Thickness (DFT) is essential for professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike. The Wet Film Thickness to Dry Film Thickness Calculator simplifies this process, allowing users to easily determine the required dry film thickness based on their wet film measurements and the solids by volume (SBV) of their coating.
This intuitive tool enables accurate calculations, ensuring that you apply the correct amount of material for optimal performance. Whether you’re working on a small DIY project or a large-scale industrial application, our calculator is designed to help you achieve the perfect finish every time.
WFT to DFT Calculator
Example Calculations
Example 1: Coating with WFT of 9.2 mils
Let’s say you have a coating with a Wet Film Thickness (WFT) of 9.2 mils (233.6 µm) and a Solids by Volume (SBV) of 65%. To find the Dry Film Thickness (DFT), you would use the formula:
DFT = WFT × SBV
Calculation in Mils:
DFT = 9.2 mils × 0.65 = 5.98 mils
Calculation in Microns:
DFT = 233.6 μm × 0.65 ≈ 151.8 μm
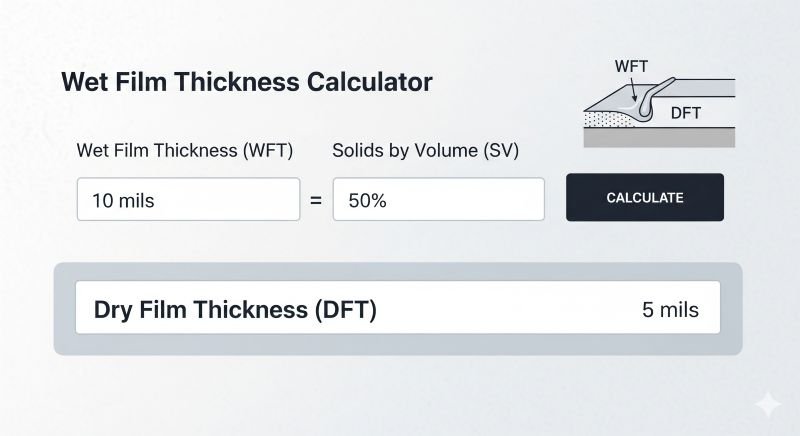
Example 2: Coating with WFT of 12 mils
Now, consider a coating with a Wet Film Thickness (WFT) of 12 mils (304.8 µm) and an SBV of 50%. To calculate the DFT:
DFT = WFT × SBV
Calculation in Mils:
DFT = 12 mils × 0.50 = 6.00 mils
Calculation in Microns:
DFT = 304.8 μm × 0.50 = 152.4 μm
Example 3: Coating with WFT of 8.5 mils
Lastly, if you have a coating with a Wet Film Thickness (WFT) of 8.5 mils (215.9 µm) and an SBV of 75%, the calculations would be as follows:
DFT = WFT × SBV
Calculation in Mils:
DFT = 8.5 mils × 0.75 = 6.38 mils
Calculation in Microns:
DFT = 215.9 μm × 0.75 ≈ 161.9 μm
The Physics of Coating Solidification
When paint is applied, it consists of “Solids” (the protective resin and pigment) and “Volatile Organic Compounds” (solvents). As the paint dries, the solvents evaporate into the atmosphere. The Dry Film Thickness (DFT) is the measurement of what remains.
The Standard Formula
The mathematical relationship used in this calculator is based on the following equation:
$$DFT = \frac{WFT \times \text{Volume Solids %}}{100}$$
If thinning has occurred, the formula adjusts to account for the increased liquid volume:
$$DFT = \frac{WFT \times \text{Volume Solids %}}{100 + \text{% Thinner Added}}$$
Why Accuracy Matters in Protective Coatings
In industrial sectors across Australia—from structural steel in Perth to marine assets in Sydney—following the AS/NZS 3894.3 standard for site testing of protective coatings is mandatory.
1. Avoiding Premature Failure
If an inspector measures a WFT that is too low, the resulting DFT will not meet the specification. This leads to “holidays” or pinholes where corrosion can start.
2. Solvent Entrapment
Applying too much wet paint can “trap” solvents under the surface skin. This causes the coating to remain soft or develop bubbles, a common issue in high-build epoxy systems.
3. Cost Management
Over-applying paint by just 20 microns across a large structural project can result in thousands of dollars in wasted material. Using a WFT gauge and this calculator ensures you apply exactly what is required.
Quick Reference: Common Volume Solids
| Coating Type | Typical Volume Solids (%) |
| Zinc-Rich Primer | 60% – 65% |
| High-Build Epoxy | 75% – 85% |
| Polyurethane Topcoat | 50% – 60% |
| Water-Based Acrylic | 35% – 45% |
Technical Tip for Inspectors
Always take your WFT measurements immediately after application. Solvents begin to evaporate the moment the paint leaves the spray tip. Waiting even 60 seconds can result in a false “thin” reading on your comb gauge.