Welding Cost Calculator
For any welding operation in fabrication industry, understanding the costs associated with different methods is crucial for making informed decisions. Whether you’re managing a project or running a welding business, knowing how to evaluate costs can help you optimize your operations and improve profitability. Today, we introduce a handy interactive calculator designed to simplify the cost evaluation process.
Welding Cost Calculator
Results
Why Cost Evaluation Matters
Cost evaluation in welding involves analyzing various factors, including labor, materials, and operational efficiency. By calculating these costs, you can determine which welding method is more economical for your specific needs. This is especially important when comparing different electrodes, such as E71T-1 and E7018, which may have varying deposition rates and costs.
Key Factors to Consider
- Welding Amperage: The amperage used affects the energy consumption and overall cost.
- Labor Cost: This includes wages and overhead associated with the workforce.
- Deposition Rate: The amount of weld metal deposited per hour.
- Operating Factor: Efficiency of the welding process.
- Gas Flow Rate: The rate at which shielding gas is used.
- Gas Cost: The price per cubic foot of the shielding gas.
Example Calculation
Let’s say you are evaluating the cost of using an E71T-1 electrode versus an E7018 electrode for a project. Here’s how you can use our calculator to analyze the costs.
Input Values
- Welding Amperage: 300 A
- Labor Cost/Hr: $45
- Deposition Rate: 10.2 lbs/hr
- Operating Factor: 0.45
- Gas Flow Rate: 40 cu ft/hr
- Gas Cost: $0.02/cu ft
Step-by-Step Calculation
Calculation Steps
- Calculate Labor Overhead:
- Labor Cost = $45
- Calculate Variable Costs:
- Labor & overhead Contribution:
- Labor Contribution = (Labor & Overhead Cost/Hr)/Deposition Rate x Operating Factor
- = $9.80
- Electrode Cost:
- Electrode Cost per lb/Deposition Efficiency
- 1.78/0.87 = $2.05
- Gas Contribution:
- Gas Contribution = (Gas Flow Rate (Cu ft/hr) x Gas Cost/Cu ft)/ Deposition Rate Ibs/hr)
- (40*0.02)/ 10.2
- Gas Contribution = 40 cu ft/hr × 0.02 = $0.08
- Labor & overhead Contribution:
- Total Variable Cost:
- Total Variable Cost = Labor & overhead Cost + Electrode + Gas Contribution
- Total Variable Cost = 9.80 + 2.05 + 0.08 = $11.93
Results
Using this calculator, you find that the total variable cost per pound of deposited weld metal is approximately $11.93.
Deposition efficiency (DE)
Deposition efficiency (DE) is the percentage ratio of welding electrode/ wire used to the amount of weld metal deposited, and to be calculated using following formula:
- DE= Weight of Weld Metal/ Weight of Electrode Used
Welding Operating Factor (Welding Efficiency)
Welding efficiency, often referred to as the operating factor, is a critical measure in welding processes. It represents the effectiveness of the welding operation in terms of how much time is actually spent on welding versus the total time taken, including setup, downtime, and other non-welding activities.
Read this post on Detailed explanation of Welding Efficiency & Its Calculation.
Key Points About Welding Efficiency (Operating Factor)
- Definition:
- The operating factor is calculated as the ratio of actual welding time to the total time spent on the task. It is usually expressed as a percentage or a decimal.
- Formula:
- Operating Factor=Actual Welding Time/ Total Time
- Typical Values:
- Operating factors can vary widely depending on the welding method, skills of the welder, and the complexity of the task. Typical values range from 0.25 to 0.85 (or 25% to 85%).
- Importance:
- A higher operating factor indicates better efficiency and productivity, meaning more time is spent actually welding rather than on setup or waiting.
- It helps in cost estimations and efficiency improvements in welding operations.
- Factors Affecting Operating Factor:
- Welder Skill Level: More experienced welders tend to have higher efficiencies.
- Type of Welding: Different processes (MIG, TIG, Stick) have different efficiencies based on their nature and application.
- Setup Time: The time taken to prepare for welding can significantly affect the operating factor.
- Equipment: The quality and suitability of the equipment being used can impact efficiency.
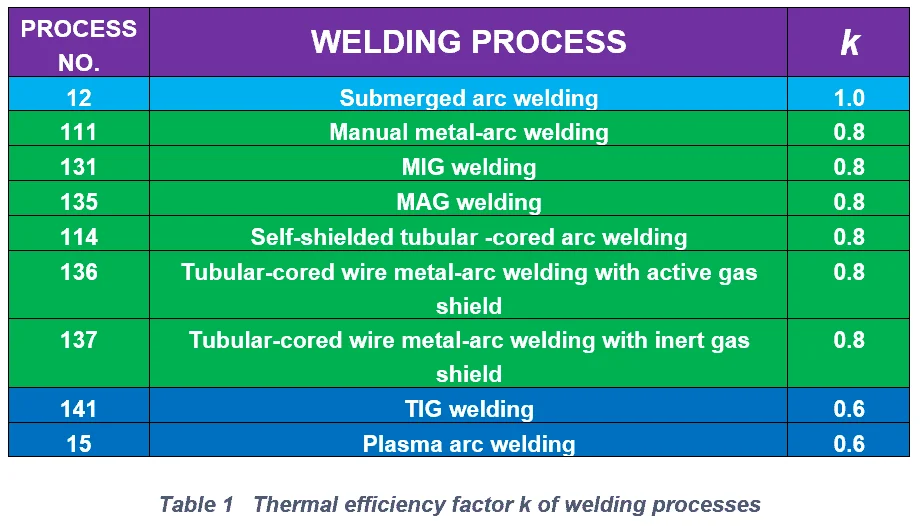
Welding Efficiency of Different Welding Processes
Welding Efficiency of Different Welding Processes are given in the below table.